Concurrency in timed usage models for system testing in the automotive domain
Project Description
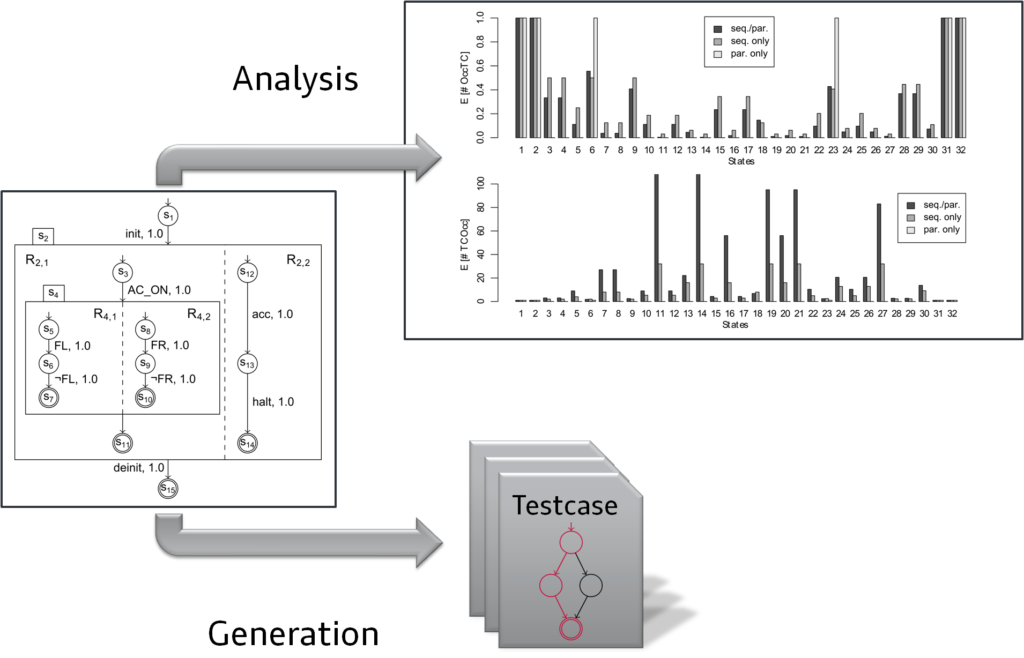
Modern vehicles are equipped with many functions that, e.g., increase the effeciency of the car, provide convenience for the driver or increase the safety. Such functions process many different information from various sensors and control specific parts of the vehicle. They are often distributed and highly interconnected, i.e., they consist of different parts that run concurrently and cooperate in order to provide the desired functionality. Furthermore, due to the distributed nature of such functions and their high degree of interconnection, their complexity is high. Disregarding their degree of complexity, they have to run correctly and in case of errors fall back into a fail-safe state in order to prevent any harm for the driver, passangers or any other persons involved. Thus a high quality is demanded from functions within an automobile. In order to receive indicators on the function’s quality, it has to be tested. Statistical model based testing with Markov chain usage models (or usage models in short) represents a method that allows to test complex functions or systems in general in a manageable and understandable way. The goal of the project is to apply usage models to test selected automotive systems. Thereby, concurrent aspects of the system under test (SUT) shall be considered explicitly in order to boost the overall test process: concepts shall be specified and implemented, that allow their explicit handling during model specification, analysis and test case generation.
Project Period
- 2012-10-01 – 2016-03-31
Project Members
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Reinhard German
Dr.-Ing. Daniel Homm
Involved institutions
AUDI AG
INI.FAU
Related Publications
- Florian Bock, Daniel Homm, Sebastian Siegl und Reinhard German, “A Taxonomy for Tools, Processes and Languages in Automotive Software Engineering,” Computer Science & Information Technology, pp. 241-256, Januar 2016
- Daniel Homm und Reinhard German, “Analysis of Hierarchical Semi-Markov Processes with Parallel Regions,” 18th International GI/ITG Conference on Measurment, Modelling and Evaluation of Computing Systems and Dependability and Fault-Tolerance (MMB & DFT 2016), Münster, Germany, April 2016 (erscheint)
- Daniel Homm, Jürgen Eckert und Reinhard German, “Combining Time and Concurrency in Model-Based Statistical Testing of Embedded Real-Time Systems,” Software Engineering and Formal Methods, Berlin Heidelberg, York, United Kingdom, pp. 22-31, 2015
- Daniel Homm, Jürgen Eckert und Reinhard German, “Concurrent Streams in Markov Chain Usage Models for Statistical Testing of Complex Systems,” 30th ACM Symposium On Applied Computing (SAC 2015), Salamanca, Spain, 2015